| Home Prev |  InControl 4.01.01 Administration Guide InControl 4.01.01 Administration Guide
|
Next |
|---|
Before a NetWall or NetShield firewall can be brought under InControl control, a Remote Management object that allows that control usually must be created in the firewall's cOS Core configuration. This chapter describes how that object is created and configured.
For NetShield see the cOS Stream Administrators Guide for details.
![[Note]](images/note.png) |
Note: Skip this chapter if using the zero touch feature |
|---|---|
|
If adding a NetWall firewall automatically to InControl using the zero touch feature, no cOS Core preparation is necessary except for making sure that the cOS Core version is no earlier than 12.00.16 and has a default configuration. This chapter can therefore be skipped. Using zero touch is fully described in Chapter 8, Zero Touch. |
Creating a Remote Management Object
To create the Remote Management object, use the following steps:Open the cOS Core management Web Interface in a browser and log in as an administrator.
Go to System > Device > Remote Management and select Add.
Choose the InControl Management (Netcon) option from the list of Remote Management object types, as shown below.
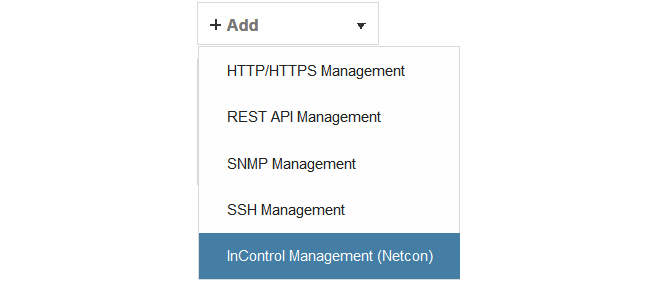
This will open up the properties display for the new InControl Management object. This is shown below with some example values already entered.
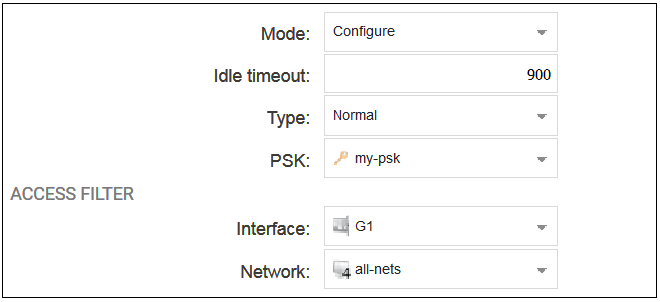
The configured properties are the following:
Mode
The following options are available: This is normally set to Configure which allows complete control.
Configure - This is the normal setting and allows InControl complete control over the configuration.
Console - This allows full control but the configuration can only be administered through InControl's console function.
Uptimepoll - This allows cOS Core to only respond to ICMP ping messages from InControl so that the online status of the firewall is correctly displayed.
This chapter will assume throughout that the Mode property is set to the value Configure.
Idle Timeout
After this many seconds of inactivity, the connection is closed.
Type
This would usually be left at the default value of Normal. However, the value Device Initiated might be used if the firewall is behind a NATing device, in which case the device itself must initiate the connection to the InControl server. This is discussed further later in this section.
The value of Zero Touch is not relevant to this section and is discussed further in Chapter 8, Zero Touch.
PSK
This is a Pre-Shared Key object that specifies the hexadecimal key that secures communication between InControl and cOS Core. This key must agree with the value of the Secret Key property of the corresponding firewall object in InControl. Creating this object is described in Appendix B, Netcon Key Generation.
Interface
The Ethernet interface on which InControl connections will be accepted.
Network
The single IP or range of source IPs from which InControl connections will be accepted.
The Device Initiated Netcon Option
The firewall itself can initiate addition to InControl by setting the Type property of the remote management object to Device Initiated. This allows another set of related properties to be set for the object, as shown below.
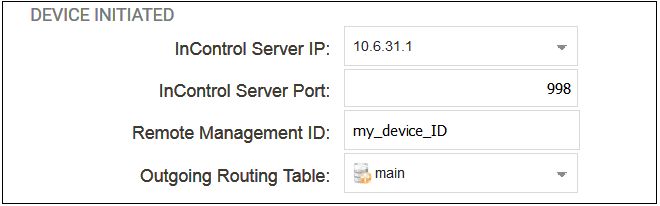
The additional properties for device initiated Netcon are the following:
InControl Server IP
This is the IP address of the InControl server which cOS Core will automatically try to contact.
InControl Server Port
The port number is used for connection on the InControl server. This default port number is 998.
Remote Management ID
Since the firewall may be behind a NATing network device, InControl cannot use the firewall's IP address in order to add it to the list of managed devices. Instead of the IP address, this Remote Management ID value will be used as the ID for the firewall and this must be specified when the firewall is defined in InControl. The value entered must match the value of Remote Management ID specified for the corresponding Remote Management object in cOS Core.
![[Important]](images/important.png) |
Important: HA cluster devices must have unique IDs |
|---|---|
|
When setting up a high availability cluster, each device (the master and the slave) must have a unique value for the Remote Management ID property. If this is not true then device initiated Netcon will fail for the cluster. |
When to Use Device Initiated Netcon
There are two methods for how a firewall can be added to InControl and brought under its control:InControl Initiates Addition
This is done by first adding a Remote Management object to cOS Core then adding the firewall to InControl using the InControl client (described in Chapter 7, Adding Firewalls). This method is also known as Server Initiated Netcon.
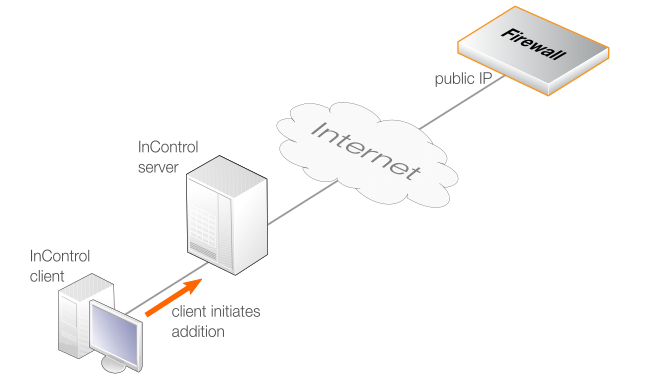
The communications between the InControl server and the firewall might be across the Internet and this is illustrated in the diagram below. In this case, the firewall must have a static public IP address since InControl is initiating the communication.
![[Note]](images/note.png) |
Note: The InControl server IP type does not matter |
|---|---|
|
With the above method of adding a firewall through the InControl client, it does not matter if the InControl server has a public IP address or is behind a NATing device with a private IP. However, the IP address of the firewall should be static. Any changes to the firewall's IP address must also be made to the firewall's properties in InControl. |
The Firewall Initiates Addition
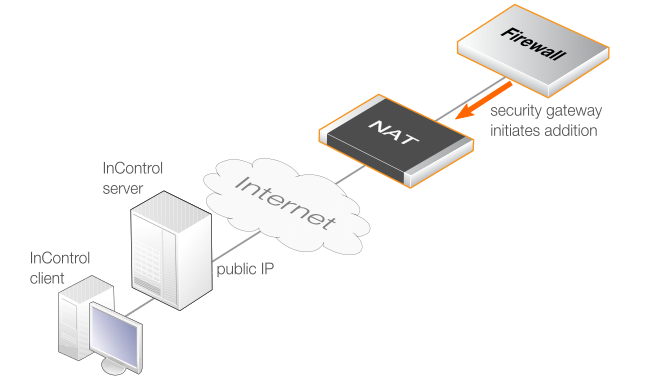
If the firewall has a private IP address and is behind a NATing device, the InControl server will not be able to connect to it across the Internet because it does not have a public IP. In this case, the approach described above will not work. Instead, cOS Core must be configured so that it initiates the addition to InControl control. This cOS Core feature is called Device Initiated Netcon (where Netcon is the proprietary Clavister protocol used between the InControl server and cOS Core).
An alternative situation where this approach should be used is when the firewall is not behind a NATing device but its IP address can change and is not known at a given point in time. In either case, Device Initiated Netcon means that the firewall does not need a static IP address and it can find the InControl server instead of the other way around.
Device initiated Netcon requires the following:
As usual, a Remote Management object must be created in the cOS Core configuration but with the Type property set to the option Device Initiated. Doing this is described later in this chapter.
A corresponding Firewall object must then be created in InControl that has the Reverse Management option enabled and has the same Secret Key and ID values as those specified in the cOS Core Remote Management object.
It also requires that the InControl server has a static public IP address if management traffic traverses the Internet. This IP is specified in the Remote Management object so that cOS Core can contact it and register that it is ready to be added.
The device initiated Netcon option is intended for use only if the firewall is behind a NATing device. Otherwise, the standard method of firewall addition should be used. The appropriate scenario for device initiated Netcon usage is illustrated in the diagram below.
Steps for Setting Up Device Initiated Netcon
When setting up device initiated Netcon, the following ordering of steps must be followed:Create a Remote Management object in cOS Core
Once the InControl Management object is configured and activated, if the Use Device Initiated Netcon option is enabled the cOS Core will immediately try to contact the specified InControl server. This will be done repeatedly at 5 second intervals until successful.
Enable Netcon in the InControl Server Interface
Device Initiated Netcon must be explicitly enabled for the InControl server. This is done with the following steps:
From the Windows Start menu, select Clavister > Clavister InControl Server Settings to open the server interface. Administrator rights will be required for changes.
Select the ReverseNetconServer options from the left-hand pane, as shown below.
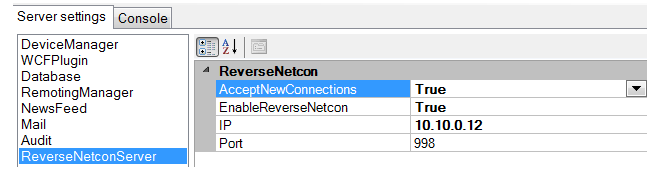
In the right-hand pane, set AcceptNewConnections and EnableReverseNetcon to a value of True. If a specific server interface is to be used for accepting incoming firewall connections then the IP address of that interface should be specified in the IP field. If any interface can be used, the IP field should be set to 0.0.0.0. The port for connections defaults to 998.
Select File > Service > Restart to restart the server. The server interface will prompt to save the changes before restarting the service.
Note that if the AcceptNewConnections option is disabled and EnableReverseNetcon is enabled, reverse Netcon will function but no new firewalls can be added to InControl.
Create a Firewall object in InControl
A corresponding Firewall object must now be created using the InControl client and this must be done after the Remote Management object is created. When specifying the InControl properties for the firewall, the following is entered:
The Online option should be enabled for the status.
The option Device Initiated option must be enabled.
The Remote Management ID property must match the Remote Management ID property specified in the cOS Core Remote Management object.
The Secret Key property must match the hexadecimal key of the PSK specified in the cOS Core Remote Management object.
Creating firewalls for both methods of addition in InControl is further described in Chapter 7, Adding Firewalls.
cOS Core finds and adds the polling firewall
Once the InControl Firewall object is created, InControl will look for a matching firewall that is polling the InControl server. When it finds the match, it will add the device as a managed firewall. This InControl client interface will then display the firewall's ID instead of its IP address. The IP address will remain unknown and is not needed for communication between InControl and the managed firewall.
Once the firewall is added using device initiated Netcon, it can be managed just like a firewall that is added to InControl in the normal way.
Device Initiated Netcon of HA Clusters Using a Single Public IP
With HA clusters, only a single public IP address may be available when InControl management is device initiated. However, this is possible using a single public IP and setting this up is described in a Clavister Knowledge Base article at the following link: